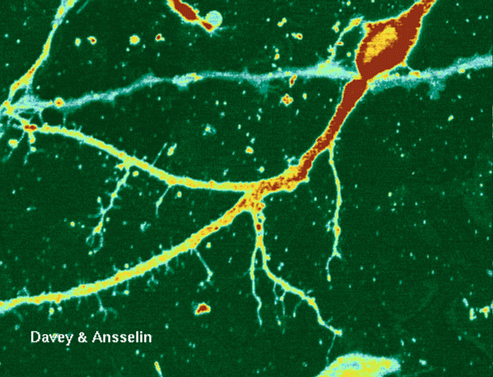
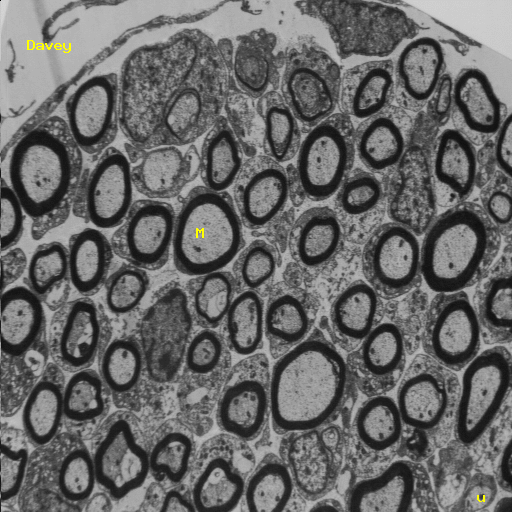
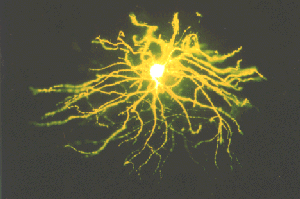
Schwann cells are the supporting cells of the PNS. Like oligodendrocytes schwann cells wrap themselves around nerve axons, but the difference is that a single schwann cell makes up a
single segment of an axon's myelin sheath. Oligodendrocytes on the other hand, wrap themselves around numerous axons at once. In addition to creating the myelin sheaths of PNS axons, Schwann cells
also aid in cleaning up PNS debris and guide the regrowth of PNS axons. To do this Schwann cells arrange themselves in a series of cylinders that serves as a guide for sprouts of regenerating
axons. If one of these sprouts encounters a cylinder the sprout will grow through the tube at the rate of 3-4 mm per day. Nonproductive sprouts simply wither away. |